Flexor Digitorum Profundus: Get an overview about it

The flexor digitorum profundus is a muscle due to which the four fingers (index, middle, ring, and little) are able to bend. It is located in the anterior compartment of the forearm. The meaning of this muscle is “deep bender of the fingers” and it is a Latin name.
There are two distinct heads of this muscle; both of them originating in the forearm. As its muscle belly is located in the forearm and it acts on the fingers, it is considered an extrinsic hand muscle.
There is a deep layer of ventral forearm muscles formed by flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicis longus, and pronator quadratus. Also you can lookout more at Healthclubfinder in regards to health, fitness, and beauty.
Now, let us have an overview of the structure of this muscle.
Structure:
This muscle originates from four sites:
- The medial surfaces of ulna
- The adjacent part of theinterosseous membrane
- The coronoid process of ulna
- The aponeurosis of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
The origin is quite broad and then the muscle takes a slightly narrow passage towards the hand and ends in fingers.
The median nerve in the forearm crosses the lateral part of the anterior surface of this muscle. There are four tendons coming out of this muscle, one to each of the fingers. These four long tendons run down the arm through the carpal tunnel and then to the fingers.
Carpal tunnel is a narrow passage in the wrist of the hand from where the median nerve passes. If there is a pressure generated on the median nerve then it results in shakiness, pain, and clumsy feeling in the hand which is called carpal tunnel syndrome.
This muscle lies deep to the Flexor digitorum superficialis so the tendons of these muscles go through the tendons of superficialis. The tendons end up attaching to the distal phalanx. That’s why it is also called the perforating muscle. Lumbricals, which are the intrinsic muscles of the hand flex the joints of the fingers and they arise from the radial side of the tendons.
The main function of this muscle is the flexion of the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. It is also associated with the flexion of the wrist. Muscle fibers are arranged in a way such that the lateral part inserts to digits 2 and 3 and the medial part of the muscle inserts into digits 4 and 5.
Innervation:
This muscle has a dual innervation.
- The medial part of the muscle is innervated by the ulnar nerve and it inserts into the fourth and fifth digits.
- The lateral part is innervated by the median nerve and it inserts into the second and third digits.
How does blood supply take place inside the muscle?
At the origin of the muscle, the blood is supplied with the inferior ulnar collateral and ulnar recurrent arteries. The ulnar artery provides blood to the superior part of the muscle belly. Branches of the ulnar, median arteries, and anterior interosseous provide blood to the rest of the part of the muscle.
What is the function of this muscle?
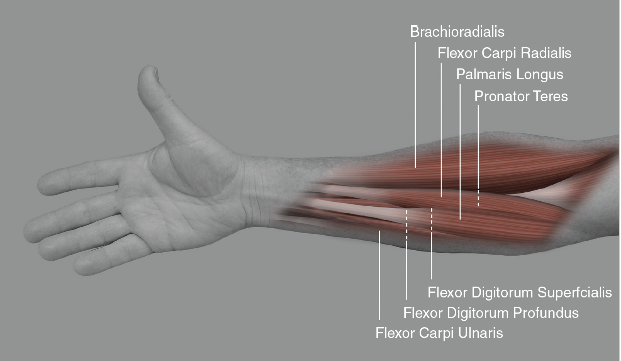
As we already told you that with this muscle, flexion of the fingers takes place. Flexion of the digits 2-4 takes place at the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints as the muscle pulls the distal phalanges towards the hand. It acts in synergy with flexor digiti minimi brevis muscles, flexor digitorum superficialis, and lumbricals.
Also, it is the wrist flexor. It helps the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum superficialis, and flexor pollicis longus muscles to bend the hand at the wrist joint.
A strong grip of the hand is established and maintained with flexor digitorum profundus.
Let’s have a quick look at the summarization.
Origination: Originates in the anterior surface of ulna, interosseous membrane
Insertion: It inserts into palmar surfaces of distal phalanges of the four fingers.
Action: Finger and Wrist flexion
Innervation: Median nerve and Ulnar nerve
That’s it, here was all the information you need to know about flexor digitorum profundus.





