Tesla, NIO and Renault: electrifying results in Green NCAP rating
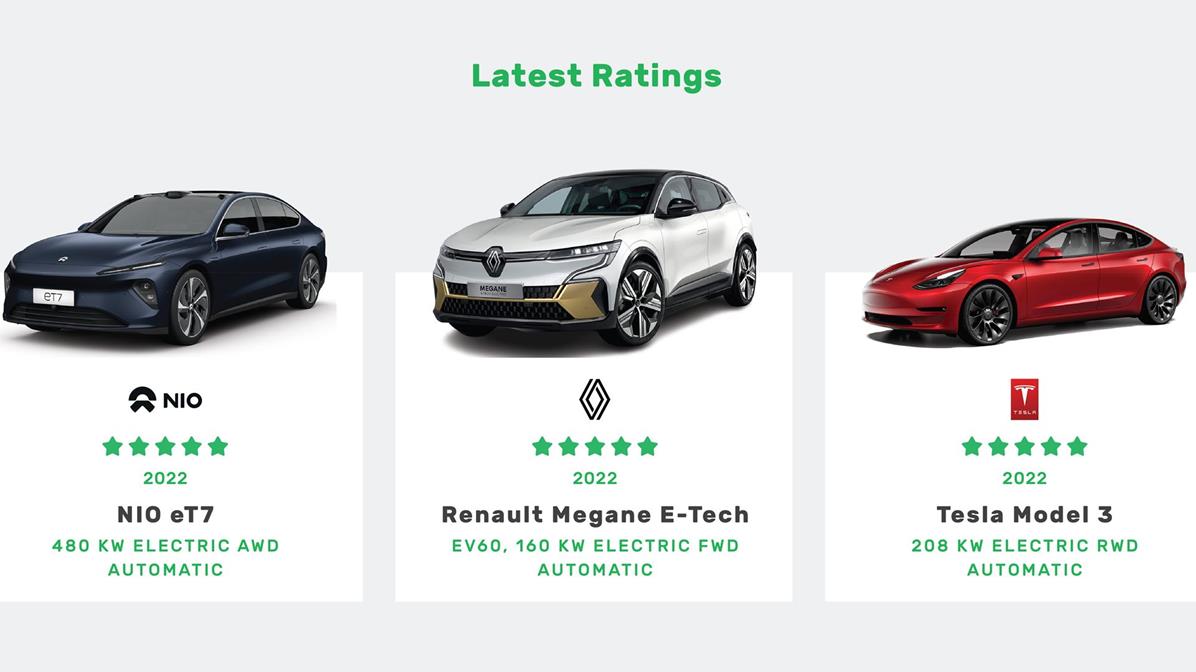
Today, Green NCAP publishes the results of three very competitive electric vehicles; the Tesla Model 3, the new-to-market NIO eT7 and the Renault Megane E-Tech 100% electric. All vehicles received an impressive five stars under the Green NCAP sustainable rating scheme, achieving nearly maximum scores due to the high energy efficiency of their electric powertrains, far exceeding the ratings of conventional cars. The results also prove that manufacturers’ investment into electric vehicles can create a choice for consumers that considers both the environment and energy efficiency, but at the same time delivers the enjoyment, comfort, and power necessary to suit today’s journeys.
The Tesla Model 3, with a battery capacity of 60 kWh, single motor, rear wheel drive and a power of 208 kW has a wide and sporty appeal. It is the smallest vehicle of the Tesla range and the brand’s first model to be tested by Green NCAP. The car achieved high energy efficiency, not only in the Cold and Warm WLTC+ laboratory tests, but also in the challenging Highway Test with a very impressive result of 21.1 kWh/100 km. The Tesla’s small frontal area and aerodynamic shape work to the vehicle’s advantage, although in the WLTC+ test cycle at a winterly -7°C because of the high demands of cabin heating, comfort and battery protection management, consumption increases by 72% and driving range is reduced significantly. Despite this and the car’s relatively high mass, its result proves that it has been designed with special attention made to efficiency and driving range.

Green NCAP rewards Tesla’s impressive performance with a Weighted Overall Index of 9.8 out of 10 and a well-deserved 5 Green stars.
NIO is a relative newcomer to the European market but already makes a strong statement with its fully equipped eT7, potentially targeting Tesla lovers. The car comes with two motors and all-wheel drive, a formidable power output of 480 kW and a huge 100 kWh battery. But this all adds weight, and the NIO tips the scales at 2.4 tons. In the laboratory WLTC+ test, the eT7 exactly matched its declared range of 580 km. Again, despite its high mass the eT7 demonstrates high overall efficiency. Under cold winter conditions (WLTC+ test at -7°C), just like the Tesla, the consumption is increased by 72% and this results in an expected driving range of about 340 km.
Despite its high mass, the NIO eT7 is impressive and confidently receives a Weighted Overall Index of 9.6 out of 10 and a well-deserved 5 Green stars.
Green NCAP tested the Renault Megane E-Tech EV60 with a battery capacity of 60 kWh, single motor, and front wheel drive. With a power of 160 kW and a spacious interior it is sure to have broad appeal, particularly with its low energy consumption figures. The values in the standard Cold and Warm WLTC+ tests are impressive, but, as with the NIO eT7, they rise notably in the Highway Test with its dynamic high power demand phases. The results of the performed short urban trip are noteworthy as this Megane used just 11.8 kWh/100 km. In the -7°C laboratory test, the vehicle’s consumption increased by 78% compared to the standard test and with 30 kWh/100 km finds itself between the measured values of the other two tested cars.
The Renault Megane E-Tech fully demonstrates, like Tesla’s Model 3 and NIO’s eT7, excellent performance and collects 9.6 out of 10 points in the Weighted Overall Index and a well-deserved 5 Green stars.
All three of these vehicles receive Green NCAP’s top marks due to the absence of polluting exhaust gas emissions and their remarkable energy efficiency scores, as well as the relatively low greenhouse gas emissions of European electricity production.
‘This latest round of Green NCAP testing clearly proves that electric vehicles are an excellent consumer choice in the quest for ensuring a cleaner and more sustainable environment. They score far higher than those with conventional powertrains. However, affordability is still a challenge. We call on manufacturers to further improve the efficiency of cabin heating in winter conditions, as this is shown to have a significant impact on driving range. The efficiency of the on-board charger constitutes a hidden cost for consumers and here the industry also needs to strive for higher numbers,’ says Dr. Michiel van Ratingen, Secretary General of Euro NCAP and Green NCAP.
Editor’s Note
For full results, visit www.GreenNCAP.com.
For media information, please contact Cordelia Wilson @ media@GreenNCAP.com.
Follow us online and on social media:





